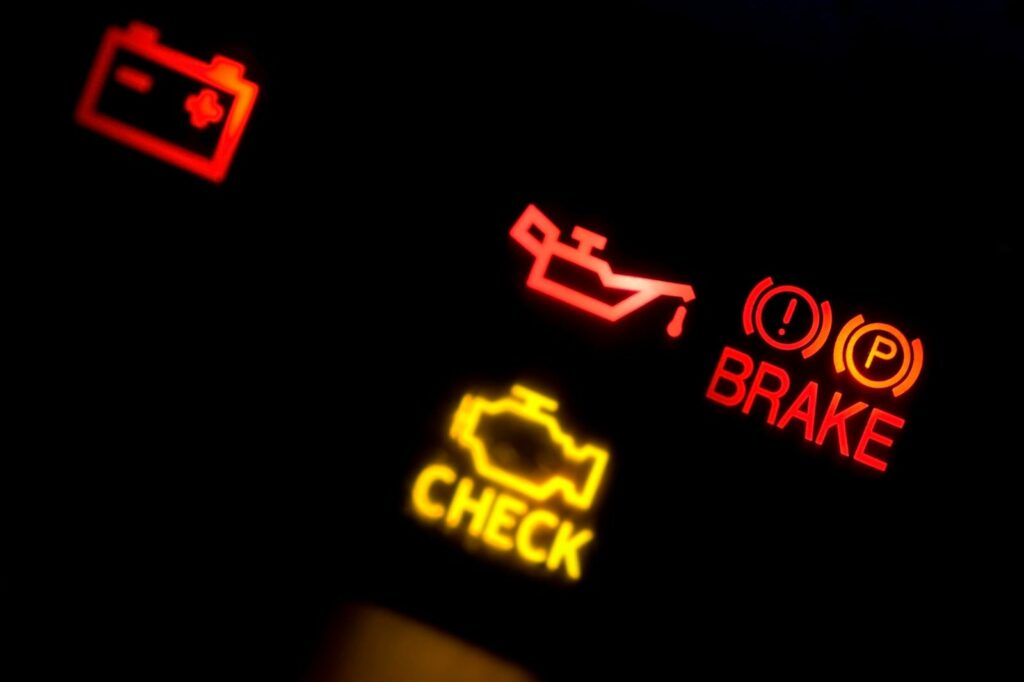
Introduction
Welcome to our guide on solving common electrical problems in your car. In this post, we’ll walk you through the most common electrical issues that you may encounter with your vehicle and provide step-by-step instructions for how to diagnose and fix them. But before we dive in, it’s important to note that working on a car’s electrical system can be dangerous if you don’t know what you’re doing. So, if you’re not comfortable with the process or don’t have the necessary tools, it’s best to seek professional help.
Step 1: Check the Battery
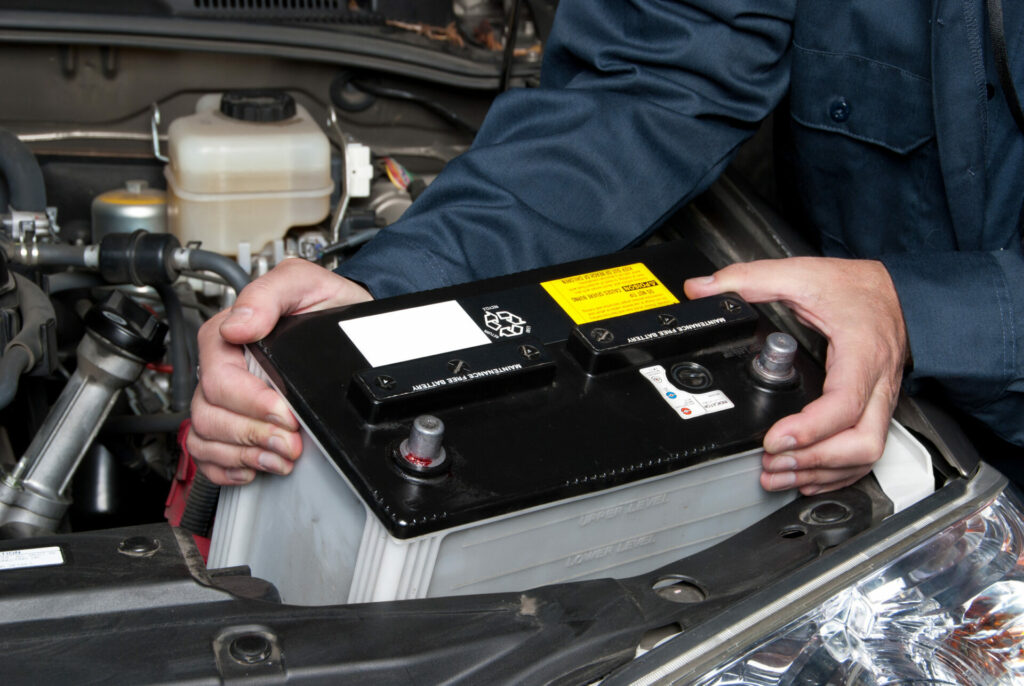
The first step in troubleshooting any electrical problem in your car is to check the battery. A dead battery is the most common cause of electrical issues in a vehicle. To check the battery, use a voltmeter to measure the voltage. A fully charged battery should have a voltage of around 12.6 volts. If the voltage is lower than 12.6, it may be time to replace the battery.
Step 2: Check the Alternator
The alternator is responsible for charging the battery and providing power to the car’s electrical system. If the alternator is not working properly, it can cause a number of problems, including a dead battery, dimming headlights, and a whining noise from the engine. To check the alternator, use a voltmeter to measure the voltage at the battery terminals while the engine is running. The voltage should be between 13.5 and 14.5 volts.
Step 3: Check the Starter
A faulty starter can cause a variety of problems, including a clicking noise when you turn the key, a grinding noise when you turn the key, or no noise at all. To check the starter, turn the key to the “on” position and listen for a clicking or grinding noise. If you hear a clicking noise, the starter may be faulty. If you hear a grinding noise, the starter solenoid may be faulty.
Step 4: Check the Fuses
A blown fuse can cause a variety of electrical problems in your car, including a dead battery, dimming headlights, and a whining noise from the engine. To check the fuses, locate the fuse box in your car and use a voltmeter to check for continuity. If there is no continuity, the fuse is blown and needs to be replaced.
Step 5: Check the Wiring
A damaged or corroded wire can cause a variety of electrical problems in your car, including a dead battery, dimming headlights, and a whining noise from the engine. To check the wiring, use a voltmeter to check for continuity and check for any visible damage or corrosion. If there is damage or corrosion, the wire will need to be replaced.
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve walked you through the most common electrical problems that you may encounter with your vehicle and provided step-by-step instructions for how to diagnose and fix them. Remember, working on a car’s electrical system can be dangerous if you don’t know what you’re doing, so if you’re not comfortable with the process or don’t have the necessary tools, it’s best to seek professional help. With the proper tools and knowledge, you can save yourself a lot of time and money by solving the common electrical problems in your car.